Connector lines – responsible for transmitting electricity from the site’s solar panels – required immediate replacement to restore the 1,200-acre solar complex to full operational capacity.
GPRS Utility Locating Enables Efficient Collector Line Replacement at 1,200-Acre Texas Solar Farm
GPRS Utility Locating Enables Safe and Efficient Collector Line Replacement at 1,200-Acre Texas Solar Farm
A solar energy facility in East Bernard, Texas, spanning approximately 1,200 acres, experienced widespread damage to underground collector lines due to wildlife activity. These lines—responsible for transmitting electricity from the site’s solar panels—required immediate replacement to restore full operational capacity.
Before repairs could begin, the damaged lines had to be accurately located. GPRS Project Managers Scott Moore and Miguel Campos, alongside Area Manager Keith Knoblock, were contracted to perform subsurface utility locating across the vast site.
“Whoever did the installation work wasn’t the company that we were contracted with,” Moore explained. “When they buried the lines, they did a great job keeping everything in order, everything in line, but they didn’t put anything in conduit. These lines are about the size of like a cable TV line, and so what happened is the wildlife in that environment would like to have dinner via those lines, so they were shorting out and burning up a lot of these combiner boxes and fun stuff like that.”

The first step in replacing damaged collector lines in a solar farm is finding the buried lines.
Locating Damaged Collector Lines Using Electromagnetic (EM) Technology
The GPRS team utilized electromagnetic (EM) locators rather than ground penetrating radar (GPR) for this project. EM locators are particularly effective for tracing metallic utilities by detecting the electromagnetic signals they emit. These tools are critical in environments where traditional locating methods are limited due to utility damage or complex site conditions.
EM locators can function in two primary modes: Active and Passive.
- Active Mode enables precise tracing, identification, and depth estimation of buried metallic lines by directly applying a signal to the utility using a transmitter.
- Passive Mode detects signals naturally radiated by utilities or induced by ambient electromagnetic energy. This mode is typically employed for locating unidentified utilities prior to excavation.
In this case, due to physical damage—chewed insulation, melted segments, and shorted conductors—many collector lines could not carry an active signal.
“Since a lot of these lines were melted, chewed through, things like that, really you couldn’t actively locate them,” Moore said. “So, we were basically locating these lines with our passive methods, which turned out to be just the quickest way to handle this job.”
Understanding EM Passive Signal Sources
Passive EM locating depends on ambient signals originating from one of three sources:
1. Power
- Current through live electrical conductors
- Cathodic protection systems
- Stray return currents from transmission systems
Note: A power signal does not definitively confirm the presence of a utility. The signal must be traced to a known source or structure for positive identification.
2. Radio
- Conductive materials acting as antennas for atmospheric radio transmissions
- Active phone lines
- Stray currents using pipes or metallic structures as return paths
Note: Radio Mode cannot determine depth. If a radio signal is detected, induction techniques may be required for accurate tracing.
3. Rebar and Embedded Reinforcement
- Reinforcing mesh or bar may reflect or re-radiate signals, leading to false positives
- Signal strength adjustments and elevation changes can isolate the actual utility signal
GPRS Project Managers use signal strength discrimination and sweep pattern refinement to ensure accurate utility identification, even under complex passive signal conditions.
Accelerated Project Timelines and On-Site Coordination
The urgency of the repair project required tight coordination between GPRS and the solar operator’s repair crews, who were on-site to immediately excavate and replace the damaged lines after GPRS located them.
The damaged collector lines were replaced with new, conduit-encased conductors designed to withstand wildlife intrusion and environmental wear.
Due to the efficiency of GPRS’ SIM-certified utility locating protocols and real-time field decisions, the locating team completed their work well ahead of schedule.
“We got to where we were weeks ahead of their rate of pace, which they were happy with,” Moore said.
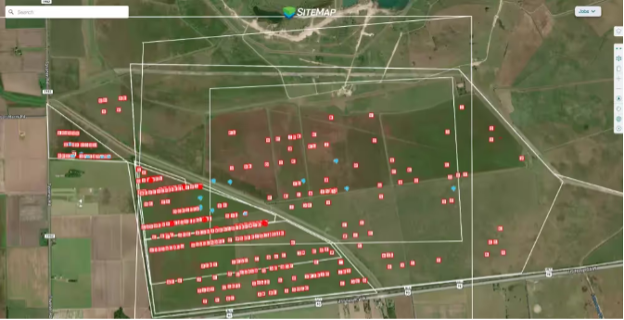
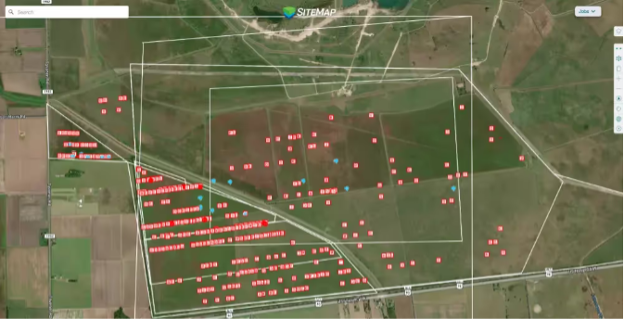
GPRS found the connector lines on the solar project and uploaded their utility map to SiteMap® so that the operations team could find and repair the damaged ones.
Data Capture and Project Documentation with SiteMap®
In addition to physically marking the collector lines with spray paint and flags, the GPRS team documented all findings in SiteMap® (patent pending), GPRS’ secure infrastructure management platform.
SiteMap® consolidates subsurface utility data into a centralized digital environment. Accessible from any computer, tablet, or smartphone, SiteMap® provides real-time visibility into underground infrastructure, enabling project teams to manage, plan, and execute safely and efficiently.
By incorporating GPRS’ utility locating data into SiteMap®, the solar farm operator now has access to verified, georeferenced utility mapping. This documentation reduces the risk of damage during future maintenance or upgrades and supports compliance with safety and regulatory requirements.
SiteMap® helps eliminate costly errors caused by incomplete records or miscommunication across teams. For this Texas solar installation, having accurate, readily accessible collector line locations will streamline all future excavation, maintenance, and asset management activities.
Overall, the East Bernard project demonstrates how GPRS’ advanced utility locating services support critical infrastructure repairs in the renewable energy sector. When conventional records are missing or outdated—and physical damage limits traditional tracing methods—EM locating, passive sweep techniques, and real-time documentation via SiteMap® provide a complete solution.
From solar farms to industrial facilities, GPRS Intelligently Visualizes The Built World® to keep infrastructure projects on time, on budget, and safe.
What can we help you visualize?
